1983
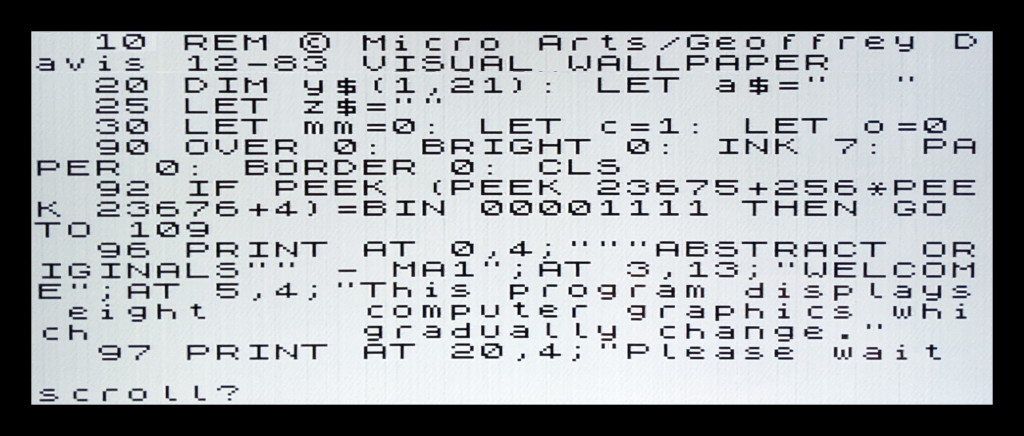
Geoff Davis programmed the menu-driven Visual Wallpaper in December 1983, which because the first Micro Arts release MA1 “Abstract Originals” in 1984. See above.
Lynn Hershman Leeson – digital artist and filmmaker (US). Created Lorna (1983–84) the first interactive piece using Videodisc, a precursor to DVD on 12” discs, and was the first artist to incorporate a touch screen interface in her artwork Deep Contact (1984–1989).
Electra (Électra) exhibition at Musée de la Ville de Paris, Trocadéro, 1983-84. Sonia Sheridan and Greg Gundlach, generative systems, Arts and Science. Artist Michèle Gauthier Carr-Brown worked with Sheridan and Gundlach in Paris in 1983 as a student, using Quantel (Lumina) Paintbox systems for the first time. This art work is in the Micro Arts Magazine 1984, and is the first artist published work using Paintbox.
Jeremy Gardiner – innovative art with plotted drawings, at Middlesex Polytechnic, using a Prime 550 computer and a Calcomp plotter. Introduced to computers by Patrick Purcell (who left UK for MIT Media Lab) and Brian Reffin Smith at the RCA’s Department of Design Research, founded by George Mallen.
Roy Ascott – La Plissure du Texte. An early pioneer of digital arts, his first telematic project was La Plissure du Texte (1980, exhibited at Electra (Electricity and Electronics in the Art of the XXth Century) exhibition (Paris, France 1983-84). This was an online work of ‘distributed authorship’ involving 14 nodes all over the world, each with each ascribed a fairytale character, with Ascott starting a multistrand narrative, in a magnified version of the Surrealist cadavre exquis. The narrative ran for three weeks. Electra also featured work by Brian Reffin Smith.
Telematics are computer-mediated telecommunications networks, now used for vehicular and other fleet management.
Jeremy Gardiner – Digital Totems exhibition at GE Hirst Research Centre, subsequently these and other works displayed in Electra 83 (Paris), London galleries and Boston USA.
Ellen R. Sandor founded artists’ group called (art)n who created a new art form, called PHSColograms (pronounced “skolograms”), 3D barrier-screen computer-generated photographs and sculptures. “I had the gut instinct that the world was going digital,” Sandor recalls. This realization led her to collaborate with top personalities in the digital world to produce innovative art and science visualisations.
Paul Brown – Sculpture Simulation – 2D print on paper, of a 3D computer simulation of a free-standing sculpture.
Brian Reffin Smith – interactive artworks at the Musée d’art Moderne de la Ville de Paris. Later invited by the French Ministry of Culture to help with art education, and was later appointed to a teaching post in the École Nationale Supérieure D’art (National Art School).
Mark Wilson – first SIGGRAPH show. Wilson had many computer art shows in the 1980s, including 1984, 1985 “The Artist and the Computer,” Louisville Art Gallery, USA; 1985 “Five with Byte,” Pittsburgh Plan for Art, USA. Also see 1980.
AARON – Harold Cohen exhibitions at major museums around the world, including Britain’s Tate Gallery in 1983, National Museum of Wales. 1983, Arnolfini Gallery, Bristol. Also Brooklyn Museum Installation, four drawing machines running, over 650 drawings sold (at ‘democratic’ prices) to the visitors, while Cohen worked on a 55 feet painting from a large drawing.
AARON is one of the longest running AI systems as Cohen began work on it in 1968. Ran on a VAX 750 minicomputer. Used a turtle robot to draw lines on the floor, which could then be coloured in by Cohen. All sizes could be created from cards to wall murals. In the 1970s, AARON created abstract drawings, and the forms became more sophisticated as Cohen continued to work on the code. Cohen was awarded the ACM SIGGRAPH Distinguished Artist Award for Lifetime Achievement in 2014.
Stephen Scrivener – Untitled (1983). Computer Printout (in CAS archive).
John Lansdown appointed Senior Visiting Fellow at the Department of Architectural Science, University of Sydney from 1983.
Halaby began to focus on the relationship of art to the technology of its time. She acquired a small personal computer, an Amiga, and found programming painting in motion with sound a hugely beautiful and absorbing project. “I could put in my paintings a more complete impression of what I see and hear of my experiences of life.”
Samia Halaby – Kinetic painting created by programming not by using animation software, using a Commodore Amiga.
Bill Viola becomes a teacher in Advanced Video at the California Institute of the Arts, in Valencia (US). Video art increasingly using computer effects.
David Em, the American artist, created digital art at California Institute of Technology (Caltech) from 1984 until 1988. Previously, he was Artist in Residence from 1977 at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Steve Hawley (of London Video Arts LVA) – video The Science Mix, with Tony Steyger, shown at the Stedelijk and MoMA New York, as part of the Second Link, the first international touring video art show.
Pete Shelley, the Buzzcocks punk pop band’s founder and writer, added a ZX Spectrum lyrics/graphics piece for the Homosapiens LP (banned by the BBC for being gay) coded by friend Joey Headen. It created lyrics and visuals. The computer program code was recorded as a track on the 1983 Genetic/Island vinyl LP.
Chris Seivey‘s recording of Camouflage Spectrum game was released on a vinyl single (usually a music format). Early chiptune music. An early music and computer promo (see Pete Shelley), the ‘B’ side (other side of vinyl plastic disk) contained a Spectrum ZX81 program.
Cube Quest by Simutrek combined 3D polygon graphics with animated streamed (laserdisk) backgrounds. The first arcade video game with real-time 3D computer graphics.
Dan Flavin Art Institute opens in Bridgehampton, New York, run by the Dia Art Foundation. It has nine fluorescent light works on permanent display.
Ada – computer language named after Ada Lovelace (1815–1852), credited as the first computer programmer. Made for the US Department of Defence to replace over 450 different programming languages in use.
There were many new languages in the 1980s including C++ (1983), Lisp, MATLAB, dBase 3 (1984), LabVIEW (1986), Perl (1987).
CGAL: Computer Graphics and Animation Language, in development for years, released by Peter Comninos (1 Jan. 1983, published by Teeside Polytechnic). Later used by Comninos at the Media School, Bournemouth University. Used at first as a teaching system. Commercialised in the 1990s. Used at Sheffield Psalter Lane Art College by Geoff Davis and Dr. David Elliott.
Novell NetWare Novell, Inc. introduced the multi-platform network operating system (NOS), Novell NetWare. Novell also produced Ethernet cards and was dominat in the networking market. Darren Umney used Novell NetWare to host a distributed art piece at Sheffield Psalter Lane in 1991.
Microsoft Word 1.0 – released in October for MS-DOS and Xenix. Developed from Xerox Bravo, the first WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) word processor.
MacWrite released for the Apple Macintosh.
Thinking Machines supercomputer (US). Sheryl Handler and W. Daniel ‘Danny’ Hillis founded Thinking Machines Corporation to turn Hillis’s doctoral work at MIT on massively parallel computing architectures. This supercomputer was known as the Connection Machine which resembled the workings of the human mind (at least in principle). Was the world’s fastest computer.
1G telephone network launched in the USA for the Motorola DynaTAC mobile phone. UK, Mexico and Canada followed in the next few years. See 1985.
The Road to Point Reyes was produced by Lucasfilm and Pixar. The static image, the first computer generated image in high resolution, was conceived and directed by Rob Cook, while Alvy Ray Smith, Loren Carpenter, Tom Porter, Bill Reeves, and David Salesin worked also on the fractal, hidden surface routines and shading.
InterAccess (Canada) – founded as Toronto Community-Videotex, for new practices in art and technology. It is a non-profit gallery, educational facility, production studio and also has a festival. See Telidon Art Project (1985).
Granny’s Garden – educational adventure game for the BBC Micro computer. Was very popular with teachers and so became well-known by a generation of programmers.
Nintendo Entertainment System (NES) – 8-bit video game console, first released it in Japan as the Family Computer (FC) or Famicom. A new version arrived in the US in October 1985, then rest of world.
1G telephone network launched in the USA for the Motorola DynaTAC mobile phone. UK, Mexico and Canada followed in the next few years. See 1985.
The Road to Point Reyes was produced by Lucasfilm and Pixar. The static image, the first computer generated image in high resolution, was conceived and directed by Rob Cook, while Alvy Ray Smith, Loren Carpenter, Tom Porter, Bill Reeves, and David Salesin worked also on the fractal, hidden surface routines and shading.
InterAccess (Canada) – founded as Toronto Community-Videotex, for new practices in art and technology. It is a non-profit gallery, educational facility, production studio and also has a festival. See Telidon Art Project (1985).
Digidesign Digidrums – upgrade chips for the E-Mu Drumulator offering different drum sounds. The chips could be easily switched in the hardware. This method also used in the Oberheim DX drum machine, which also allowed custom sounds with an EPROM burner. The engineers went on to develop Pro Tools.
The first MIDI drum machine, the Roland TR-909 and the first MIDI sequencer, the Roland MSQ-700 were released.
E-mu Systems Drumulator drum machine released. It was a companion to the Emulator sampling keyboard (1981). Also cheaper than the competition. A simple digital unit with EPROM- based memory for its non-editable 12-bit samples (same as Oberheim DMX).
Sound Designer from Digidesign – sound editor for the new range of sample-based instruments. Developed into Pro-Tools.
Pinball Construction Set game written by Bill Budge, a creator game where a pinball machine could be created from parts, and even the rules of physics changed. Marketed by Electronic Arts. Ran on the Apple II and later the Atari 8-bit micros and Commodore 64, IBM PC, 1985, and Macintosh, 1986.
International Soccer – first popular football game for the Commodore 64.
Blue Monday dance song released by band New Order (UK) in March by Factory Records. Recorded using an Oberheim DMX drum machine, sequenced using a ‘step-time’ sequencer in binary code. The famous bassline was played on a Moog Source, on a Powertran Sequencer. 12″ single with floppy disk-styled packaging designed by Peter Saville and Brett Wickens. Best-selling 12″ of all time including 1988 and 1995 re-releases.
ZTT Records (UK). Multimedia (mainly music) label started by record producer Trevor Horn, Jill Sinclair,) journalist Paul Morley. ZTT used the latest digital sampling and sequencing equipment and techniques to create new soundscapes for popular music.
Art of Noise (ZTT) Into Battle – Moments In Love – Beat Box. Highly produced release, much sampled since.
Frankie Goes to Hollywood (FGTH) had epic ZTT productions of the tunes Relax and Two Tribes , with lurid videos, and were among the most influential and best-selling singles of the decade.